***Current conditions: *Warm air headed northward up the East Coast is set to collide with cold air headed southward over the Great Lakes and Northeast, bringing snowfall followed by higher temperatures later in the week • A cold front is stirring up a dense fog in northwest India • Unusually frigid Arctic air in Europe is causing temperatures across northwest Africa to plunge to double-digit degrees below seasonal norms, with Algiers at just over 50 degrees Fahrenheit this week.
THE TOP FIVE
1. Crude prices fell in 2025 amid oversupply, complicating Venezuela’s future
 A chart showing average monthly spot prices for Brent crude oil throughout 2025.EIA
A chart showing average monthly spot prices for Brent crude oil throughout 2025.EIA
Oil prices largely fell throughout 2025, capping off December at their lowest level all year. Spot market prices for Brent crude, the leading global benchmark for oil, dropped to $63 per barrel last month. The reason, according to the latest analysis of the full year by the Energy Information Administration, is oversupply in the market. China’s push to fill its storage tanks kept prices from declining further. Israel’s June 13 strikes on Iran and attacks on oil infrastructure between Russia and Ukraine briefly raised prices throughout the year. But the year-end average price still came in at $69 per barrel, the lowest since 2020, even when adjusted for inflation.
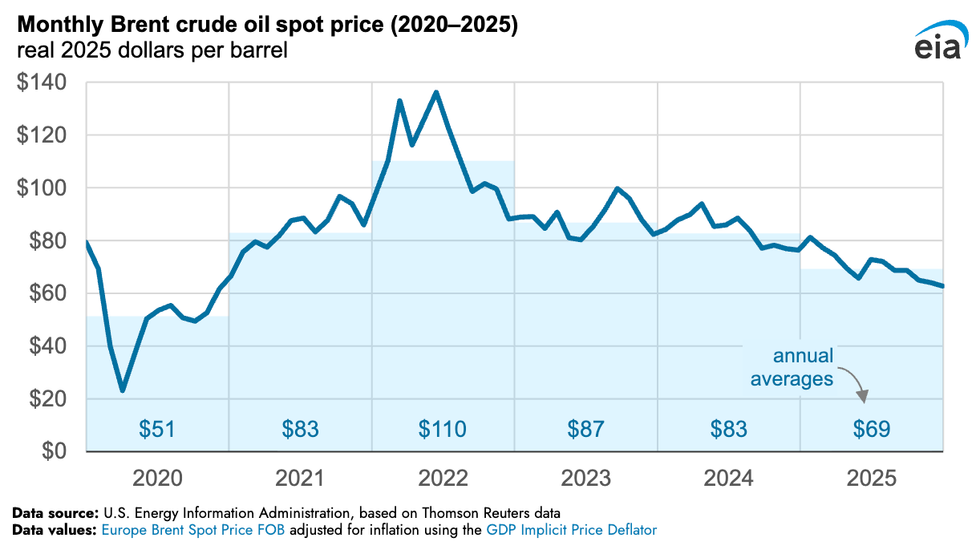 A chart showing average annual spot prices for Brent crude oil throughout from 2020 to 2025.EIA
A chart showing average annual spot prices for Brent crude oil throughout from 2020 to 2025.EIA
The price drop bodes poorly for reviving Venezuela’s oil industry in the wake of the U.S. raid on Caracas and arrest of the South American country’s President Nicolás Maduro. At such low levels, investments in new infrastructure are difficult to justify. “This is a moment where there’s oversupply,” oil analyst Rory Johnston told my colleague Matthew Zeitlin yesterday. “Prices are down. It’s not the moment that you’re like, I’m going to go on a lark and invest in Venezuela.”
2. Energy Department grants nearly $12 million to Texas metal recycling project
The Energy Department granted a Texas company known for recycling defunct tools from oil and gas drilling an $11.5 million grant to fund an expansion of its existing facility in a rural county between San Antonio and Dallas. The company, Amermin, said the funding will allow it to increase its output of tungsten carbide by 300%, “reducing our reliance on foreign nations like China, which produces 83%” of the world’s supply of the metal used in all kinds of defense, energy, and hardware applications. “Our country cannot afford to rely on our adversaries for the resources that power our energy industry,” Representative August Pfluger, a Texas Republican, said in a statement. “This investment strengthens our district’s role in American energy leadership while providing good paying jobs to Texas families.”
That wasn’t the agency’s only big funding announcement. The Energy Department gave out $2.7 billion in contracts for enriched uranium, with $900 million each to Maryland-based Centrus Energy, the French producer Orano, and the California-headquartered General Matter. “President Trump is catalyzing a resurgence in the nation’s nuclear energy sector to strengthen American security and prosperity,” Secretary of Energy Chris Wright said in a press release. “Today’s awards show that this Administration is committed to restoring a secure domestic nuclear fuel supply chain capable of producing the nuclear fuels needed to power the reactors of today and the advanced reactors of tomorrow.”
3. House set to gut energy efficiency rules for manufactured homes
Low-income households in the United States pay roughly 30% more for energy per square foot than households who haven’t faced trouble paying for electricity and heat in the past, federal data shows. Part of the problem is that the national efficiency standards for one of the most affordable types of housing in the nation, manufactured homes, haven’t been updated since 1994. Congress finally passed a law in 2007 directing the Department of Energy to raise standards for insulation, and in 2022, the Biden administration proposed new rules to increase insulation and reduce air leaks. But the regulations had yet to take effect when President Donald Trump returned to office last year. Now the House of Representatives is prepared to vote on legislation to nullify the rules outright, preserving the standards set more than three decades ago. The House Committee on Rules is set to vote on advancing the bill as early as Tuesday night, with a full floor vote likely later in the week. “You’re just locking in higher bills for years to come if you give manufacturers this green light to build the homes with minimal insulation,” Mark Kresowik, senior policy director of the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, told me.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
4. China’s nuclear industry starts 2026 with one reactor finished and two more started
The newest reactor at the Zhangzhou nuclear station in Fujian Province has officially started up commercial operation as China’s buildout of new atomic power infrastructure picks up pace this year. The 1,136-megawatt Hualong One represents China’s leading indigenous reactor design. Where once Beijing preferred the top U.S. technology for large-scale reactors, the Westinghouse AP1000, the Hualong One’s entirely domestic supply chain and design that borrows from the American standard has made China’s own model the new leader.
In a sign of just how many reactors China is building — at least 35 underway nationwide, as I noted in yesterday’s newsletter — the country started construction on two more the same week the latest Hualong One came online. World Nuclear News reported that first concrete has been poured for a pair of CAP1000 reactors, the official Chinese version of the Westinghouse AP1000, at two separate plants in southern China.
5. Japan’s first floating offshore wind turbines come online
Back in October, when Japan elected Sanae Takaichi as its first female prime minister, I told you about how the arch-conservative leader of the Liberal Democratic Party planned to refocus the country’s energy plans on reviving the nuclear industry. But don’t count out offshore wind. Unlike Europe’s North Sea or the American East Coast, the sharp continental drop in Japan’s ocean makes rooting giant turbines to the sea floor impossible along much of its shoreline. But the Goto Floating Wind Farm — employing floating technology under consideration on the U.S. West Coast, too — announced the start of commercial operations this week, pumping nearly 17 megawatts of power onto the Japanese grid. Japanese officials last year raised the country’s goal for installed capacity of offshore wind to 10 gigawatts by 2030 and 45 gigawatts by 2040, Power magazine noted, so the industry still has a long way to go.
THE KICKER
Beavers may be the trick to heal nature’s burn scars after a wildfire. A team of scientists at the U.S. Forest Service and Colorado State University are building fake beaver dams in scorched areas to study how wetlands created by the dams impact the restoration of the ecosystem and water quality after a blaze. “It’s kind of a brave new world for us with this type of work,” Tim Fegel, a doctoral candidate at Colorado State, who led the research, said in a press release.