Introduction: The 95% Accuracy Challenge
Building an OCR system that works in a lab is easy. Achieving 95%+ accuracy in production across thousands of real-world documents with faded ink, crumpled paper, and varying layouts is a different challenge entirely.
At VisionParser, we’ve processed a very large volume of documents, from receipts and invoices to tax forms and passports. We learned what separates demos from production-grade OCR systems.
The most common failures aren’t about low accuracy on perfect documents. They’re about hallucinations (AI confidently extracting data that doesn’t exist), brittle parsers that break when templates change, and false confidence (systems that report 98% accuracy but can’t identify which 2% i…
Introduction: The 95% Accuracy Challenge
Building an OCR system that works in a lab is easy. Achieving 95%+ accuracy in production across thousands of real-world documents with faded ink, crumpled paper, and varying layouts is a different challenge entirely.
At VisionParser, we’ve processed a very large volume of documents, from receipts and invoices to tax forms and passports. We learned what separates demos from production-grade OCR systems.
The most common failures aren’t about low accuracy on perfect documents. They’re about hallucinations (AI confidently extracting data that doesn’t exist), brittle parsers that break when templates change, and false confidence (systems that report 98% accuracy but can’t identify which 2% is wrong).
This guide shares the patterns that took us from 85% to 95%+ accuracy across 50+ document types: field-level confidence scoring, self-correction loops, mathematical validation, and schema-driven architecture.
Architecture Overview
Our OCR pipeline follows a clear flow:
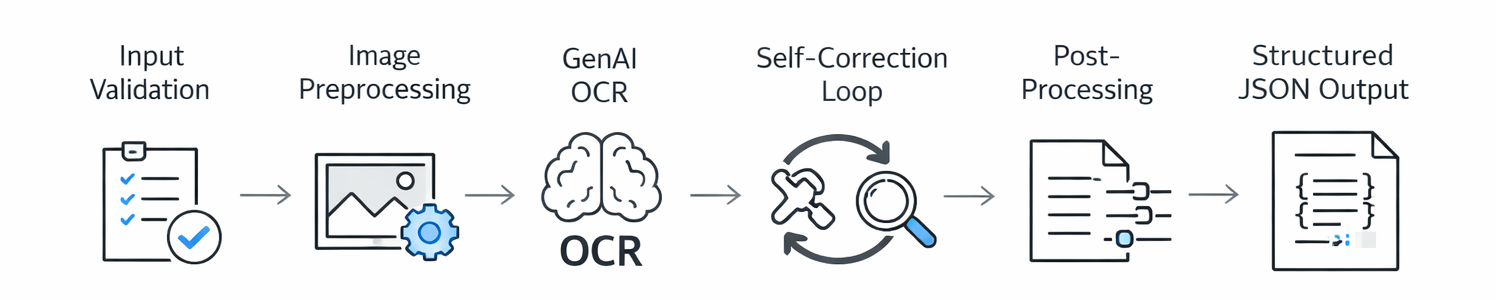
Each stage has a specific job and can fail gracefully without crashing the pipeline.
Why GenAI Over Traditional OCR?
Traditional OCR engines like Tesseract extract text but struggle with context, layout, and structure. GenAI vision models understand documents differently. They can:
- Interpret ambiguous characters from context (is it an "8" or a "B"?)
- Navigate complex layouts (tables, multi-column documents)
- Output structured JSON directly
- Improve through prompt engineering instead of retraining
The tradeoff is latency. Our pipeline takes 5-15 seconds per document versus under 1 second for traditional OCR. For high-accuracy batch processing, this cost is acceptable.
Core Design Patterns
Magic Byte Validation: We validate file types using magic bytes, not client headers. Client-provided MIME types can be spoofed, misconfigured, or simply wrong. Magic bytes provide reliable file type detection based on actual file content.
Memory-Only Processing: We eliminated cloud storage uploads for document parsing, saving 200-500ms per request. Files stay in memory, only metadata persists to PostgreSQL.
Selective Preprocessing: Upscale JPEG (lossy compression benefits from it), skip PNG and PDF (already high quality). Simple rule, 15% accuracy boost on low-quality images.
Schema-Driven Architecture: JSON schemas generate Pydantic models, AI prompts, and API docs automatically. Adding a new document type takes under 5 minutes with zero code.
The Accuracy Playbook: 5 Core Mechanisms
Achieving 95%+ accuracy requires layering multiple validation mechanisms.
Field-Level Confidence Scoring
Most OCR systems return one confidence score for the entire document. "92% confidence" tells you nothing about which fields are wrong.
We give every field its own 5-level confidence score:
| Level | Score | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
very_high | 0.95 | Machine-printed, clearly visible |
high | 0.80 | Clear with minor shadows/fading |
medium | 0.65 | Requires interpretation (handwritten) |
low | 0.40 | Significant clarity issues |
very_low | 0.25 | Barely legible |
This enables smart automation. One payment processing client uses this to auto-approve high-confidence fields, flag medium confidence for quick review, and route low confidence to specialists. Result: 80% straight-through processing with 99%+ accuracy.
Self-Correction Loop
When GenAI outputs don’t match our schema (wrong types, missing fields), we don’t fail the request. Instead, we ask the AI to fix its own mistake.
The process: Extract → Validate → If invalid, send error details back to AI → Re-extract → Validate again. If still invalid, return the original with low confidence (graceful degradation).
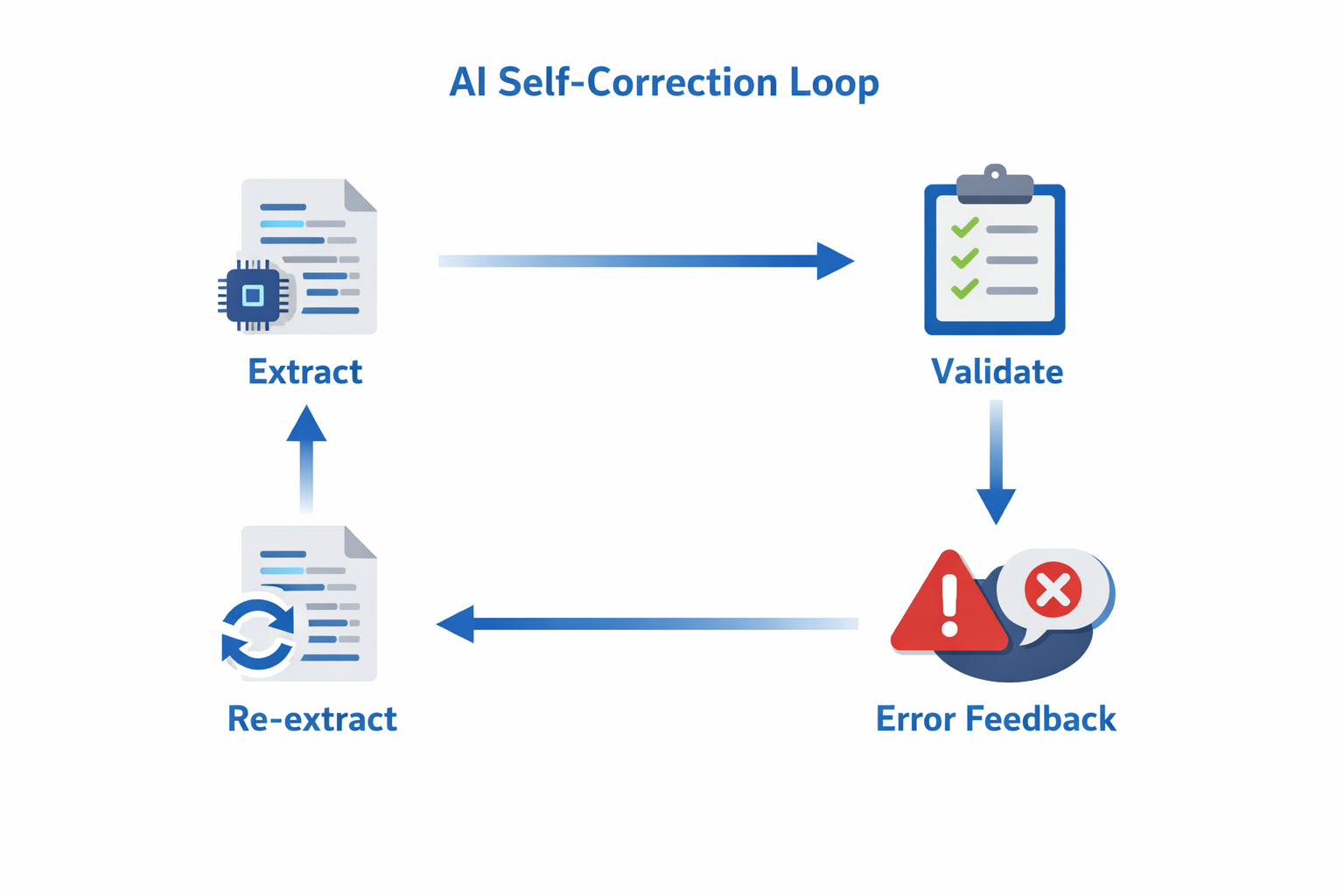
Success rate: ~85% of validation errors get fixed on the first retry.
Why it works: The AI sees precise feedback ("expected float, got string ‘1,234.56’") and reformats correctly. Common fixes include number formatting, date standardization, and type conversions.
This single mechanism improved accuracy by ~15% and cut manual review queues significantly.
Mathematical Cross-Validation

GenAI can hallucinate plausible but incorrect numbers. We prevent this for financial documents by embedding validation rules: line_total = quantity × price, total = sum(items) + tax - discount.
Important: We don’t auto-fix math errors. If numbers don’t add up, we keep them but lower confidence to "low." Why? The document itself might have errors.
Example: Invoice shows subtotal $175, tax $17.50, total $195 (should be $192.50). We flag it with low confidence, and the client’s AP system routes it for a 10-second human review instead of auto-approving.
Few OCR systems do this. Most extract fields independently and miss these patterns.
Null-First Strategy
In production, precision beats recall. It’s better to return null than hallucinate data.
Traditional OCR always returns something, leading to dangerous hallucinations. Missing PO number? AI invents one. Faded total? AI guesses $0.00.
Our approach: Explicitly tell the AI "return null if not clearly visible" and apply post-processing rules (e.g., if value is 0.0 with low confidence, convert to null).
| Document | Without Null-First | With Null-First |
|---|---|---|
| Faded receipt tip | $0.00 (wrong) | null (honest) |
| Missing PO number | "N/A" (hallucinated) | null (correct) |
Impact: 20% fewer false positives. Clients prefer honest null over wrong data.
Schema-Driven Prompt Generation
Managing prompts for 50 document types manually is unsustainable. Update validation logic? Edit 50 files.
We auto-generate prompts from JSON schemas. Define a document once with field names, types, and descriptions. The prompt generator creates extraction instructions automatically.
Benefits: Single source of truth, zero duplication, instant updates across all document types. Discover a better prompting pattern? Update the generator once, all 50 types improve immediately.
This turns prompt engineering from an art into a repeatable software discipline.
Scaling to 50+ Document Types
Supporting 50 document types traditionally means 200-300 hours of development: write models, prompts, tests, and docs for each type. Update validation logic? Edit 50 files.
Code Generation Pipeline
We treat document schemas as data, not code. Define once, generate everything.
JSON Schema → Pydantic Models → AI Prompts → API Docs → In-Memory Registry
Adding a new document type: Create JSON schema (5 minutes), restart API. Done. No Python code, no manual prompts, no documentation updates.
What we support: 50+ document types across financial documents, tax forms, identity docs, shipping labels, healthcare forms, and more. 316+ unique fields maintained in ~15KB of JSON.
Why it works: Schema changes propagate instantly. Update validation logic once, all 50 types benefit. Type safety guaranteed by Pydantic. API docs auto-generate.
This let us scale from 5 to 50 document types in 6 months without growing the team.
Production Resilience
Production systems face hostile conditions. Our resilience strategy:
Input Validation: Validate file types via magic bytes (not headers), enforce size limits (30MB), restrict formats (PDF/PNG/JPEG), check page counts.
Intelligent Retries: 3 attempts with exponential backoff, per-retry timeouts, status polling every 250ms. GenAI APIs fail; plan for it.
Graceful Degradation: Always return something useful. Image upscaling fails? Use original. Self-correction fails? Return original with low confidence. Background tasks fail? Log but don’t block response.
Domain Validation: IBAN format checks, address standardization, confidence-aware null conversion.
Debug Logging: Store comprehensive metadata (request ID, processing time, file size, errors) in PostgreSQL JSONB for post-mortem analysis.
Production Learnings
After processing a very large volume of documents, here’s what worked and what we’d change.
What Worked
Schema-driven architecture: 10x faster development. Update validation logic once, all 50 types benefit instantly.
Self-correction: 15% accuracy boost, 40% fewer manual reviews. Works best for structural errors (wrong types) rather than content errors (misread text).
Field-level confidence: Clients achieve 82% straight-through processing with 99%+ accuracy by auto-approving high-confidence fields.
Memory-only processing: 300ms latency reduction, simpler infrastructure.
GenAI over traditional OCR: Higher per-request cost but massive savings on engineering and manual review. The lower accuracy of traditional OCR creates 3-5x higher manual review costs, which more than offsets the API price difference.
What We’d Change
Dual-track API earlier: Separate endpoints for new functionality prevent breaking changes.
Customization layer sooner: Enterprise clients need per-customer schemas. Should have been day-one architecture.
Aggressive caching: Could cache layout analysis for identical templates, saving 30-50% of API costs.
Key Metrics
- Latency: 7-10s average (6s p50, 14s p95)
- Accuracy: 95-98% standard fields, 90-95% complex fields
- Self-correction: 15% of requests trigger it, 85% succeed
- Confidence calibration:
very_highfields are 98% correct,highare 92% correct
Actionable Takeaways
If you’re building an OCR pipeline, prioritize these patterns:
1. Field-Level Confidence Scoring Return confidence per field (very_low to very_high), not per document. Enables smart automation: auto-approve high-confidence, flag low for review.
2. Self-Correction Loops Validate → Feed errors back to AI → Retry. 85% success rate, 15% accuracy boost overall.
3. Mathematical Validation For financial docs: embed rules (total = sum(items) + tax), flag discrepancies with low confidence.
4. Null-First Prompting Precision over recall. Tell AI "return null if not clearly visible" and post-process low-confidence zeros to null.
5. Schema-Driven Design JSON schemas auto-generate models, prompts, and docs. Add document types in minutes, not hours.
6. Graceful Degradation Always return something useful. Upscaling fails? Use original. Correction fails? Return with low confidence.
7. Magic Byte Validation Validate file types via magic bytes, not client headers.
Recommended Stack: FastAPI, Pydantic, GenAI vision models, PostgreSQL + JSONB, Redis caching.
Common Pitfalls: Trusting client headers, single confidence scores, no retry logic, hardcoded parsers, ignoring math validation, always returning something (use nulls!).
Conclusion
Achieving 95%+ accuracy in production isn’t about finding a perfect model. It’s about layering validation mechanisms, embracing uncertainty through confidence scoring, and building systems that self-correct.
GenAI has fundamentally changed document understanding. We’ve moved from brittle template-based extraction to context-aware systems that improve through prompt engineering rather than model retraining.
Next frontiers: multi-page context awareness, complex table extraction, better handwriting recognition, real-time streaming, and more precise confidence calibration.
At VisionParser, we’re pushing OCR accuracy boundaries while keeping it affordable and accessible. Want to see field-level confidence, mathematical validation, and self-correction in action?
Try the VisionParser API at visionparser.com. We support 50+ document types with the patterns described in this guide built-in. Learn more in our API documentation.
Check out our interactive demo.