- 10 Nov, 2025 *
task 1 - Introduction to Defensive Security
Defensive security is concerned with two main tasks:
- Preventing intrusions
- Detecting intrusions and responding properly
Blue teams are part of the defensive security landscape.
Some of the tasks that are related to defensive security include:
User cyber security awareness: Training users about cyber security helps protect against attacks targeting their systems.
Documenting and managing assets: We need to know the systems and devices we must manage and protect adequately.
Updating and patching systems: Ensuring that computers, servers, and network devices are correctly updated and patched against any known vulnerability (weakness).
Setting up preventative security devices: firewall and intrusion prev…
- 10 Nov, 2025 *
task 1 - Introduction to Defensive Security
Defensive security is concerned with two main tasks:
- Preventing intrusions
- Detecting intrusions and responding properly
Blue teams are part of the defensive security landscape.
Some of the tasks that are related to defensive security include:
User cyber security awareness: Training users about cyber security helps protect against attacks targeting their systems.
Documenting and managing assets: We need to know the systems and devices we must manage and protect adequately.
Updating and patching systems: Ensuring that computers, servers, and network devices are correctly updated and patched against any known vulnerability (weakness).
Setting up preventative security devices: firewall and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) are critical components of preventative security. Firewalls control what network traffic can go inside and what can leave the system or network. IPS blocks any network traffic that matches present rules and attack signatures.
Setting up logging and monitoring devices: Proper network logging and monitoring are essential for detecting malicious activities and intrusions. If a new unauthorized device appears on our network, we should be able to detect it.
Security Operations Center (SOC)
Threat Intelligence
Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR)
Malware Analysis
question
which team focuses on defensive security?
blue team
task 2 - areas of defensive security
in this task, we will cover the following:
- Security Operations Center (SOC), where we cover Threat Intelligence
- Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR), where we also cover Malware Analysis
Security Operations Center (SOC)
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a team of cyber security professionals that watches a network and its systems to detect malicious events. Some of the areas of interest for a SOC are the following:
- Vulnerabilities
- Policy violations
- Unauthorized activity
- Network intrusions

Threat Intelligence
- In this context, intelligence refers to the information you gather about potential or actual enemies. A threat is any action that could disrupt or adversely affect a system. Threat intelligence collects information to protect from potential adversaries. The purpose being to create a threat-informed defense. Different adversaries have different goals, some want to steal customer data; others might want to halt production in a petroleum refinery.
Intelligence needs data. Data has to be collected, processed, and analyzed. Data is collected from local sources like network logs and also public sources such as forums. Data processing arranges all of it into a good format for analysis. The analysis phase seeks to find out more information about the attacks and their motivations; also, it seeks to create a list of recommendations and actionable steps to respond with.
Learning about your adversaries lets you know how they work; tactics, techniques, and procedures. As a result of threat intelligence, we can identify the threat actor and predict what they will do next. With this knowledge we can prevent future attacks and have a response strategy.
Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR)
This section is about Digital Forensics and Incident (DFIR) and we will cover:
- Digital Forensics
- Incident Response
- Malware Analysis
Digital Forensics
With the spread of all different types of computers a new branch of forensics was born, digital forensics or computer forensics.
In defensive security, the focus is on analyzing attacks and who did it. This includes:
- File systems
- System memory
- System logs
- Network logs
Incident Response
An incident is typically when a data breach or attack happens but can also be a misconfiguration, intrusion attempt, or policy violation. Examples of a cyber attack include an attacker making our network or systems inaccessible, defacing (changing) the public website, and data breach (stealing company data). How would you respond to a cyber attack? Incident response specifies how to respond in each case. The goal is always to reduce damage and recover as soon as possible. Ideally, you would develop a plan that is ready for incident response.
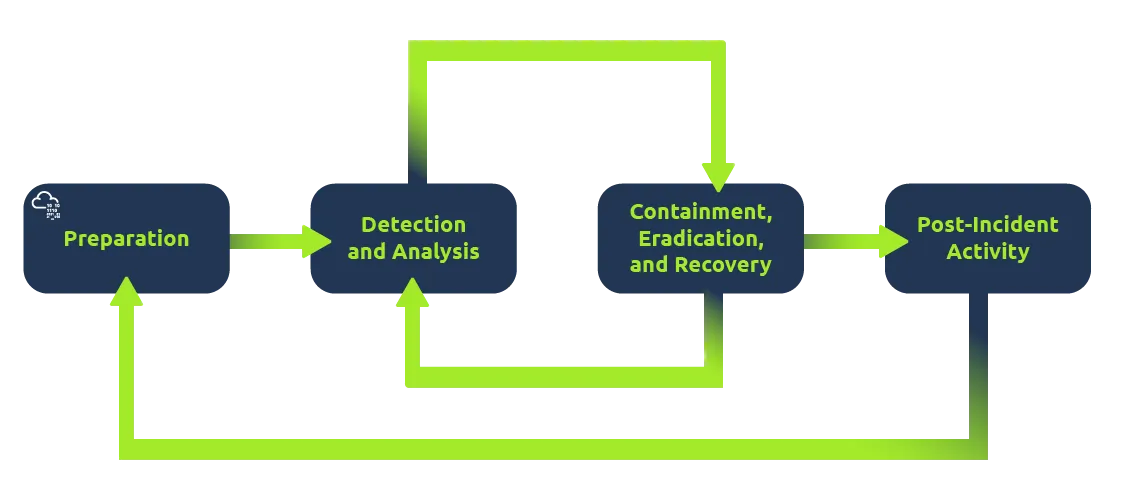
The four major phases of the incident response process are:
- Preparation
- Detection and analysis
- Containment, Eradication, and Recovery
- Post-Incident Activity
Malware Analysis
“Malware” is short for malicious software. Software is any programs, document, or files you can send over a network or save on a disk. Malware types include:
Virus: a piece of code (part of a program) that attaches itself to a program. It is designed to spread from one computer to another and works by altering, overwriting, and deleting files once it infects a computer. The result ranges from the computer becoming slow to unusable.
Trojan Horse: a program that shows one desirable function but hides a malicious function underneath. For example, a victim might download a video player from a shady website that gives the attacker complete control over their system.
Ransomware: a malicious program that encrypts the user’s files. Encryption makes the files unreadable without knowing the encryption password. The attacker offers the user the encryption password if the user is willing to pay a “ransom.”

Malware analysis aims to learn about such malicious programs using various means:
Static analysis works by inspecting the malicious program without running it. This usually requires solid knowledge of assembly language (the processor’s instruction set, i.e., the computer’s fundamental instructions). 1.
Dynamic analysis works by running the malware in a controlled environment and monitoring its activities. It lets you observe how the malware behaves when running.
questions
Q1. What would you call a team of cyber security professionals that monitors a network and its systems for malicious events?
- Security Operations Center
Q2. What does DFIR stand for?
- Digital Forensics and Incident Response
Q3. Which kind of malware requires the user to pay money to regain access to their files?
- ransomware
task 3 - practical example of defensive security
The Scenario
Let us pretend you are a Security Operations Center (SOC) analyst responsible for protecting a bank. This bank’s SOC uses a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tool, which gathers security-related information and events from various sources and presents them in one dashboard. If the SIEM finds something suspicious, an alert will be generated.

Not all alerts are malicious, however. It is up to the analyst to use their expertise in cyber security to investigate which ones are harmful.
For example, you may encounter an alert where a user has failed multiple login attempts. While suspicious, this kind of thing happens, especially if the user has forgotten their password and continues to try to log in.
Additionally, there might be alerts related to connections from unknown IP addresses. An IP address is like a home address for your computer on the Internet—it tells other computers where to send the information you request. When these addresses are unknown, it could mean that someone new is trying to connect or someone is attempting unauthorized access.
Click the View Site button
You will see this:
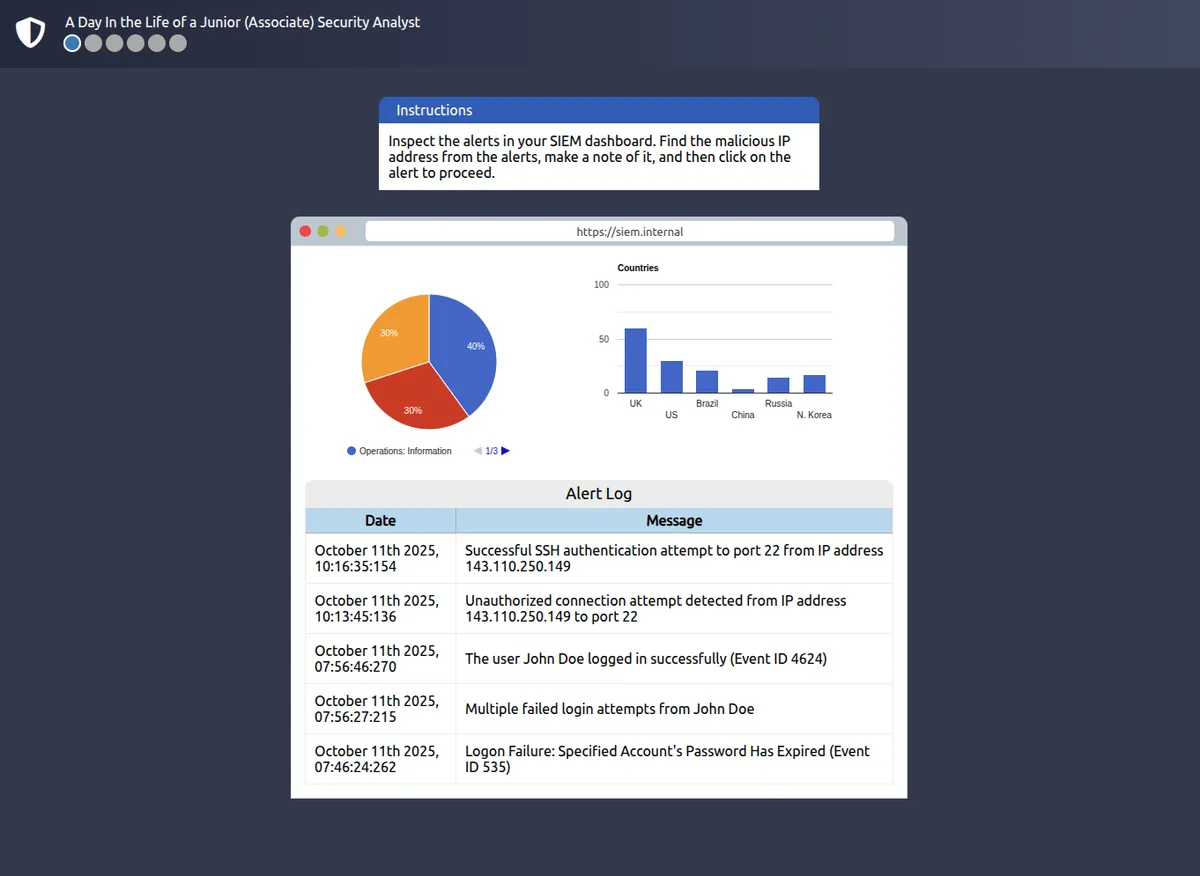
Select the one with IP address 143.110.250.149 in the alert log
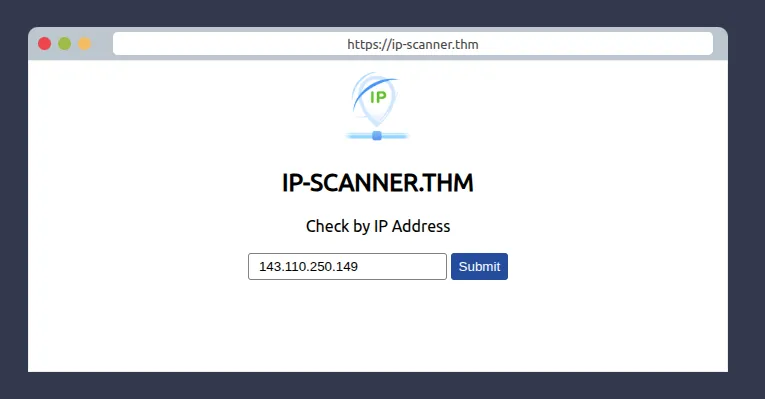
Enter 143.110.250.149 here

Select to escalate this to Will Griffin
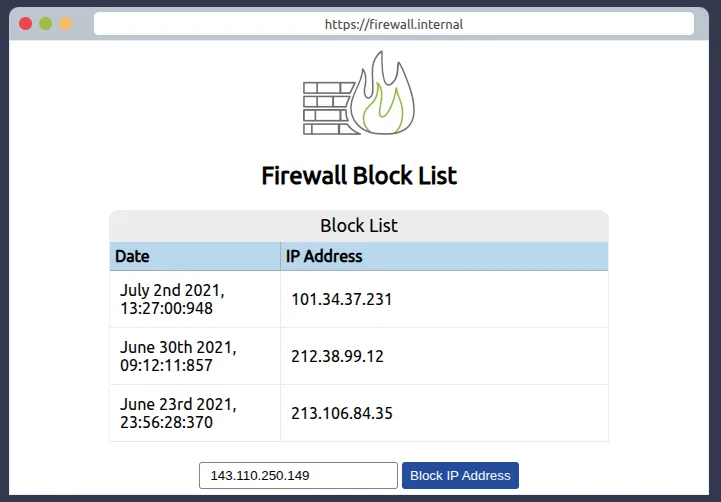
Enter 143.110.250.149 here to block it.
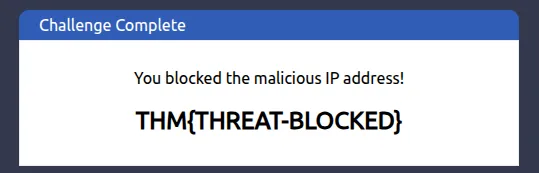
What is the flag that you obtained by following along?
THM{THREAT-BLOCKED}