1748-9326/20/11/114074
Abstract
Silicate weathering induces atmospheric CO2 sequestration through alkalinity release, which is Earth’s prime mechanism for regulating the climate. Marine enhanced rock weathering (mERW) seeks to accelerate this process by distributing fast-weathering silicate minerals like olivine in coastal environments, thus targeting deliberate carbon dioxide removal. However, the efficiency and environmental impact of mERW remain uncertain, as experimental studies are not capable of tracking the CO2 sequestration rate and ecological effects over sufficiently long timescales. Natural coastal environments with olivine-rich sands enable insight into long-term weathering and may serve as analogues envisioned for mERW applications. Papakōlea Beach (Hawai’i) is on…
1748-9326/20/11/114074
Abstract
Silicate weathering induces atmospheric CO2 sequestration through alkalinity release, which is Earth’s prime mechanism for regulating the climate. Marine enhanced rock weathering (mERW) seeks to accelerate this process by distributing fast-weathering silicate minerals like olivine in coastal environments, thus targeting deliberate carbon dioxide removal. However, the efficiency and environmental impact of mERW remain uncertain, as experimental studies are not capable of tracking the CO2 sequestration rate and ecological effects over sufficiently long timescales. Natural coastal environments with olivine-rich sands enable insight into long-term weathering and may serve as analogues envisioned for mERW applications. Papakōlea Beach (Hawai’i) is one of the few beaches across the world with olivine-rich sands (>80% by weight), thus providing a unique mERW analogue. We examined in situ weathering and biogeochemical cycling at Papakōlea as well as in the nearby mixed volcanic/coral sands of Richardson Ocean Park. Flow-through sediment incubations examined olivine dissolution kinetics, alkalinity release, and the fate of weathering products. High-resolution scans of weathered grains characterized olivine dissolution and surface alteration processes. Alkalinity generation from Papakōlea’s olivine sands and carbonate dissolution in Richardson Ocean Park was observed alongside dissolved inorganic carbon increases, suggesting CO2 sequestration occurs in this near-shore marine setting. However, complex biogeochemical interactions impede a precise quantification of olivine dissolution. Our findings highlight the complexity and challenges of monitoring, reporting, and verification for mERW applications in dynamic coastal settings.
Export citation and abstractBibTeXRIS
In addition to cutting anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions (Friedlingstein et al 2022), the goals of the 2015 Paris Agreement (UN 2015) require active carbon dioxide removal (CDR) from the atmosphere at the gigaton (Gt) scale by 2050 (Sanderson et al 2016, Rogelj et al 2018, Lee et al 2023). The potential of the global ocean to act as a sink and reservoir for atmospheric CO2 is receiving increased attention (Hoegh-Guldberg et al 2019), but until present, no marine CDR (mCDR) method has been implemented on a large scale. Urgent research is needed to develop affordable and ecologically safe mCDR technologies (Smith 2016, Oschlies et al 2023, Renforth et al 2023, Riebesell et al 2023), which satisfy suitable legal, social, and ethical constraints (Baatz et al 2025). However, the present scientific understanding of the sequestration efficiency and environmental impacts of mCDR is limited, and the necessary procedures for monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) remain underdeveloped (Ho et al 2023).
Ocean alkalinity enhancement (OAE) is a specific mCDR technique that aims to increase the ocean’s capacity for uptake of atmospheric CO2 through the addition of alkalinity (AT) to seawater (Hartmann et al 2013, Renforth and Henderson 2017). Increased seawater AT shifts the carbonate system equilibrium away from CO2 towards bicarbonate (HCO3−) and carbonate (CO32−) ions, allowing more CO2 to dissolve in the seawater (Wolf-Gladrow et al 2007). One proposed OAE method is marine enhanced rock weathering (mERW), in which fast-weathering minerals are distributed onto coastal and shelf sediments, where they gradually dissolve and release AT to the overlying water upon dissolution (Hartmann et al 2013, Meysman and Montserrat 2017, Renforth and Henderson 2017, Arico et al 2021).
Among the target minerals for mERW, the magnesium-silicate olivine (Mg(2−x)FexSiO4) has received attention due to its relative rapid dissolution (three orders of magnitude faster than quartz), global availability (8 Mt yr−1 production; Harben et al 2006), and high specific AT generation and CO2 sequestration (Hangx and Spiers 2009, Renforth 2012, Montserrat et al 2017, Flipkens et al 2021, Fuhr et al 2022, Geerts et al 2025). The idealized reaction equation for the dissolution of pure forsterite (Fo100, the 100% Mg endmember) and subsequent CO2 sequestration is given by:
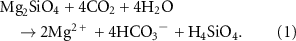
As such, 4 moles of CO2 are sequestered per mole of olivine, or equally, ∼1.25 ton of CO2 per ton of olivine. Fo92 olivine (92% Mg and 8% Fe), the most common type, has about 8% lower CO2 sequestration potential than pure forsterite due to Fe2+ oxidation consuming AT (Griffioen 2017, Renforth and Henderson 2017).
CDR via mERW takes inspiration from natural rock weathering, which sequesters about 1.5 Gt CO2 annually and leads to carbon storage that is essentially permanent over a timescale of thousands of years (Wallmann 2001, Archer et al 2009, Renforth and Henderson 2017, Penman et al 2020). mERW seeks to expedite this natural weathering process by exposing minerals to the ‘benthic weathering engine’, a set of physical, chemical, and biological processes that increase weathering rates (Meysman and Montserrat 2017, Geerts et al 2025). In systems with high hydrodynamic energy, the local bedload transport and associated physical abrasion can increase weathering rates (Gunter et al 2023, Aparicio et al 2025, England and Bach 2025). In permeable, the pore water advection driven by waves or currents can increase mineral dissolution rates by preventing the build-up of dissolution products and promoting oxic mineralization of organic matter, lowering pH and promotes weathering (Meysman and Montserrat 2017, Silburn et al 2017).
However, substantial uncertainties remain regarding the dissolution rate, net AT production, CO2 sequestration efficiency, and the release of harmful solutes when olivine-based mERW would be applied in natural environments. Potential environmental risks of olivine-based mERW may result from the release of trace metals Nickel (Ni) and chromium (Cr), which are present in olivine (Putirka et al 2011) and the impacts of pH changes on food webs and biogeochemical cycling (Blewett and Leonard 2017, Flipkens et al 2021, Ferderer et al 2022, Guo et al 2022, Jankowska et al 2024, Xin et al 2024, Zhu et al 2024). The present knowledge about olivine-based mERW is almost exclusively derived from laboratory experiments (Wogelius and Walther 1991, Pokrovsky and Schott 2000, Rosso and Rimstidt 2000) and small-scale mesocosm studies (Montserrat et al 2017, Rigopoulos et al 2018, Fuhr et al 2022, Gunter et al 2023, Bach 2024), which do not capture the full complexity of the natural seafloor environment. Moreover, the length of experimental studies and field trials (days to maximum a few years) is by default much shorter than the time over which olivine-based mERW projects will last (25–500 years; Geerts et al 2025), which makes it challenging to predict the long-term fate and impact of such projects.
In this study, we use the naturally olivine-rich beaches of Hawai’i’s Big Island (up to >80% by weight; Walker 1992) to investigate long-term olivine weathering and evaluate MRV methods for mERW in natural systems. These rare sites provide a unique analogue for assessing olivine-based mERW, including dissolution over extended timescales. During a field campaign, we applied multiple geochemical techniques to track dissolution kinetics, metal release, and AT generation. Our findings provide various insights into real-world applications, particularly the difficulty of quantifying dissolution rates in geochemically complex environments and the implications for designing reliable MRV protocols.
2.1. Study sites and field sampling
This study targeted two bays along the shore of Hawaii’s Big Island (figure 1), chosen for their contrasting sediment compositions and hydrodynamic conditions. Papakōlea beach (Pap) is located near the southern tip of the island, facing Pu’u Mahana Bay (figure 1(a)). This beach was formed by erosional material from a littoral tuff cone, older than 49 000 years (Trusdell and Lockwood 2020), from which ash shards (basaltic glass) are removed and the denser olivine phenocrysts accumulate on the beach (Walker 1992). Pu’u Mahana Bay opens directly to the South Pacific, where strong wave dynamics prevail, and water temperature remain around 27 °C all year (Grossman and Marrack 2019). In contrast, the Richardson Ocean Park (Ric) is located on the east side of Big Island (figure 1(b)) and provides a sheltered embayment with coral reefs, surrounded by a natural basalt breakwater. Sediments within the bay consist of a mixture of coral fragments, basalt sand, and olivine phenocrysts (table 1).
Figure 1. (a) Overview map of Hawaii’s Big Island with the two study sites and location from where seawater was collected. (b) Map of Papakōlea beach showing the three sampling sites (Pap E: beach sand; Pap A: surf-zone; Pap B: seabed) as well as the cliff providing the beach with newly eroded cone material. (c) Map of Richardson Bay showing the three sampling sites: (Ric A: no incubations; Ric B: mixed sediments; Ric C: calcium carbonate sand; Ric D: mixed sediments with higher olivine concentrations. (Leaflet I © Google Maps).
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image 
Table 1. Location of study sites and associated environmental parameters.
SiteStationLatitudeLongitudeWater depth (m)Sediment typeWater temperature (°C)Salinity Pu’u Mahana BayPap E18.936 26−155.64640 (dry beach)Olivine sand**—****—** Pap A18.935 76−155.64630 (swash zone)Olivine sand29.232.2 Pap B18.935 39−155.64596.4Olivine sand31.333.2
Richardson Ocean ParkRic B19.736 53−155.01393Olivine/basalt/ calcium carbonates26.533.5 Ric C19.736 76−155.01392.8Calcium carbonate sand with some basalt and olivine25.833.9 Ric D19.736 35−155.01413Olivine/basalt/ coral sand27.833.1
Sediment and pore water sampling was performed in July and August 2022. The sampling was conducted in accordance with a special activity permit (SAP 2023-15) issued by the Department of Land and Natural Resources, Hawai’i. Sediment from the oxygenated surface layer (top 5–10 cm) was collected for flow-through incubations and stored in plastic buckets with aerated overlying water. Seawater for the flow-through incubations was collected from South Point (figure 1) and incubations began within 24 h after sediment collection. Additionally, olivine grains from the Pu’u Mahana Bay layers exposed at the cliff face were collected with micro spatulas.
In situ pore water depth profiles were collected at all stations using carbon fiber push-point sampler (M.H.E. Products, East Tawas, MI, USA, Henry 2001) mounted in the seabed by SCUBA divers. Samplers were deployed at 5 cm intervals from the sediment surface to 25 cm depth, with two replicate arrays placed ∼1 m apart. Pore water samples (11 ml) were analyzed on-site for pH and dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations (section 2.3.3). The remaining pore water was filtered (0.45 µm Supor™), split into aliquots and analyzed for alkalinity (AT), dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), weathering products (DSi and dissolved Ca, Ni, and Cr) and nutrients (NOx, NH4, DSi, DIP). The chemical analysis are described in the supplementary methods.
2.2. Flow-through flux incubations
Ex situ flow-through incubations were performed to simulate the sediment–water solute exchange induced by current and wave-driven advection in permeable sediments (supplementary methods, figure S1, Lunstrum et al 2023). The flow-through set-up involved cylinders (∼1560 ml) capped and fitted with a nylon mesh (41 µm; Merck Millipore) to retain the sediment. Aerated, unfiltered seawater was circulated bottom-to-top via Tygon® tubing from 10 l HDPE jerrycans using a peristaltic pump. The equivalent linear flow rate was 1.31 × 10−4 cm s−1 (Supplementary methods). Twelve cylinders were incubated at the same time, three replicates per station from each bay and 3 seawater controls. Incubations with sand from Richardson Ocean Park ran for 5 d whereas the presumably less reactive sand from Pu’u Mahana Bay was incubated for 16 d to increase the likelihood of detecting an olivine weathering signal. The incubations were performed at ∼23 °C and in the dark to prevent photosynthesis. Temperature and salinity were monitored daily using an Aanderaa 5860 conductivity sensor.
Water samples (45 ml) were collected from the seawater reservoir every 12–70 h, with a higher temporal resolution at the beginning of the incubation. These samples were analyzed for AT, DIC, DSi, Ca, Ni, Cr, NOx, NH4, DSi, DIP. The chemical analysis are described in the Supplementary methods. Sediment-water fluxes were calculated as the change in concentration over time per unit of sediment area. A linear regression model was fitted to concentration data versus time and the obtained slope was multiplied by the volume of water in the incubations and divided by the sediment surface area (area of the cylinder opening). Flux significance was assessed at p < 0.05. The 12 h sample was excluded due to an initial concentration spike from pore water replacement. Positive fluxes indicate release of compounds from the sediment, negatives indicate uptake. After incubation, homogenized sediment from each cylinder was stored in opaque HDPE containers for later mineralogy and grain size analysis.
2.3. Analytical techniques
2.3.1. Olivine grain characterization
Olivine grains from the sediments at Pap and Ric were randomly retrieved, and qualitative imaging of dissolution features was performed using a Phenom Pro Desktop scanning electron microscope (SEM; Phenom-World B.V., The Netherlands) at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV. Olivine grains from the cliff face were subjected to more detailed characterization. First, olivine grains were separated non-destructively using heavy liquid separation prior to imaging of n = 53 grains with a FEI Quanta 250 field emission gun (FEG) ESEM. To avoid damage to the grains or loss of resolution with carbon coating, the ESEM was operated in low vacuum mode and imaged using the Large Field Detector at 5–20 kV and a 10 mm working distance. We determined the forsterite composition of 11 grains using single crystal diffraction XRD (Oxford diffraction Nova x-ray diffractometer) using an Onyx CCD detector with a resolution of 0.84 Å resolution for the Cu K-alpha x-rays. The x-ray generator was set to 50 kV and 0.8 mA. The detector distance is 62.0 mm, the oscillation width was 1.0° and the exposure time was 1.0 s. Data were analyzed using CrysalisPro, which assigned the space group as Pna2(1), as expected for olivine, and yielded unit cell parameters for each sample. These unit cell parameters are dependent on the Mg and Fe distribution in the M1 and M2 cation sites allowing estimation of the forsterite content using the a-axis dimensions. Using LAS X software on a Leica petrographic microscope, the external dimensions of each olivine grain were estimated to ±10%.
2.3.2. Sediment composition
The sediment samples from the flow-through incubations were analyzed by SEM-based automated mineralogy (Fandrich et al 2007). This procedure provides a quantification of the mineral phase concentration, grain size distribution, mineral association and mineral liberation. Mineral association describes the tendency of a mineral of interest to be conjointly found with another mineral phase, while mineral liberation describes how much of the olivine grain surface is free from contact with other minerals and is available to react with the environment. For this, separate ‘grain mounts’ were prepared by mixing 1 gram of sediment sample with 25 volume parts of EpoFix resin (Cat. No. 40200086) and 3 volume parts of EpoFix hardener (Cat. No. 40 200 088), both supplied by Struers (Struers ApS, Ballerup, Denmark). The mixture was cast in 3 cm-diameter grain mount molds and cured for 1 d at room temperature. After curing, the grain mounts were polished using Struers Tegramin 30 and carbon coated using Quorum Q150V S. The polished grain mounts were then measured using a TESCAN MIRA3 SEM equipped with a FEG located at the Geology department at Ghent University. The SEM was operated at an accelerating voltage of 25 kV, with a general probe current of approximately 0.5 nA. The acquired mineral maps were processed using TIMA 1.7.1 software (TESCAN).
3.1. Solute fluxes in flow-through incubations
The flow-through incubations revealed that AT fluxes varied widely across stations and generally showed an AT release from the sediment (figure 2). While the dry beach sand at Pap E showed no measurable AT flux, the swash zone (Pap A) and submerged seabed (Pap B) showed a mean AT release of 15 and 65 mmol m−2 d−1 respectively. At Richardson Ocean Park, stations Ric B and Ric D exhibited similar AT fluxes as Pap A and Pap B, while the carbonate-rich sediment at Ric C showed an AT release that was nearly twice as high as at other stations.
Figure 2. Sediment-water solute fluxes from flow-through incubations. Individual panels depict the flux of AT, dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), and dissolved calcium (Ca), dissolved silicate (DSi), Ni and Cr. Average values (±standard deviations) of significant fluxes per station are shown as lines, individual incubation results are shown as points. The shade of the points show fluxes that are different from zero (p < 0.05 black, p ⩾ 0.05 grey). Fluxes indicating a release from the sediment are positive (>0), while uptakes are negative (<0).
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image 
The DIC fluxes followed a similar pattern to AT, with lowest fluxes at Pap E and a wide variation between replicates at Ric C, and to a lesser extent, at Pap B (figure 2). Ca fluxes were highly variable, with a significant uptake at Pap A and a release at Ric C but should be treated with caution as the concentration changes were small relative to the analytical uncertainty. Likewise, the DIC fluxes reflect equilibration with the atmosphere during open incubations rather than true benthic fluxes. The DSi flux was always positive and comparable across stations, except for Ric C, where it was 2–3 times higher than at other stations. Measurements of Ni and Cr were limited to Pap B and Ric C, stations deemed to have the highest likelihood to show significant fluxes based on the AT data. Ni was released at both stations, with a higher efflux at Ric C, while a slight Cr uptake occurred at Pap B.
3.2. Olivine surface characterization
The olivine phenocryst-rich volcanic layers exposed in the cliffs above Pu’u Mahana Bay provide the source material that nourishes the beach. ESEM images of olivine grains retrieved from this cliff site revealed diverse morphologies, ranging from fractured fragments to well-formed crystals, some partially covered in quenched, vesicular volcanic glass (figure 3). Grain surfaces were generally rough and irregular, showing minimal smoothing. In contrast, the grain retrieved from the sediment stations at Pap and Ric showed a more weathered appearance, with textures that varied from smooth, polished surfaces (Pap E) to rough, pitted, and grooved regions with cracks and chromite inclusions (Pap A, Pap B, Ric B, Ric C, Ric D). Olivine grains retrieved from Pap were typically subangular to rounded, showing mechanical wear such as fractures, while grains from Ric retained sharp, angular edges. Notably, olivine from the swash zone (Pap E) and offshore (Pap B) at Pu’u Mahana Bay were rounded to subrounded, with smooth surfaces and no sharp edges. Grains from station Pap E grains appeared to be particularly highly polished, free of fractures and inclusions. Some grains exhibited clear dissolution features, ranging from isolated pits to interconnected chains (Pap A), often accompanied by fractures and inclusions. Single-crystal XRD analysis of grains from the cliff site indicated olivine compositions ranging from Fo92 to Fo75 (Supporting Information).
Figure 3. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of olivine (Ol) grains from different stations, showing variations in crystal morphology and surface textures. Pu’u Mahana Cliff: Olivine grains exhibit well-defined orthorhombic crystal forms with recognizable crystal faces, and some grains display epitaxially nucleated crystals and adhering volcanic glass. Pu’u Mahana Bay (Pap A, Pap B, Pap E): Olivine grains exhibit rounding as less acute edges between crystal faces, chatter marks from grain impacts, and dissolution pits. Richardson Ocean Park (Ric B, Ric C, Ric D): Olivine indicates inclusion of other minerals, such as chromite (Chr) and salt, with Ric D containing grains with higher olivine concentrations and surface etching. Red dashed boxes highlight specific areas of interest, providing detailed views of surface textures and crystal growth patterns.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image 
3.3. Sediment mineralogy and grain size distribution
Sediment mineralogy and grain size distribution differed markedly between Pap and Ric stations (figure 4). Pap sediments contained abundant forsterite olivine (68–92 wt.%), with clinopyroxene (6–23 wt.%) and carbonates (1–6 wt.%) as less abundant components, whereas orthopyroxene, plagioclase, and quartz were present in minor amounts. In contrast, Richardson Ocean Park sediments contained much higher carbonate fractions (34–70 wt.%), as expected, but also contained substantial olivine (12–31 wt.%) and clinopyroxene contents (10–20 wt.%), thus suggesting a sizeable input of mafic minerals.
Figure 4. (a) Mineral phases of sediment from incubated sediments (Carb = carbonates, Ol = olivine, Orth = orthopyroxene, Clino = clinopyroxene, Plg = plagioclase and Qtz = quartz) in fraction (wt.%) determined by automated mineralogy of incubated sediments for stations at Pu’u Mahana Bay (Pap E, Pap A, Pap B) and Richardson Ocean Park (Ric B, Ric C, Ric D). (b) Cumulative liberation by free surface area (%) of olivine classified using automated mineralogy in each station and (c) grain size (µm) distribution of olivine and carbonate grains plotted on a logarithmic scale and sampled from incubated sediments after incubations experiments.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image 
Pap and Ric sediments exhibited a wide grain size distribution, ranging from coarse sand to fine silt. In general, the Pap sites had coarser sediment than the Ric sites. At Pu’u Mahana Bay, dry beach (Pap E) and onshore (Pap A) sediments consisted of medium to coarse sand (grain size ∼350–850 µm), whereas the submerged station (Pap B) contained smaller olivine grains with a higher fraction in the medium to fine sand range (figure 4(c)). In contrast, Ric samples exhibited strong olivine peaks within the silt range (∼5–10 µm). The carbonate fragments within the Pap sediments spanned all grain sizes, but showed a clear peak within the coarse range, like the olivine. The carbonate fragments fractions at Richardson showed a bimodal pattern, with one fraction of small, silt-like particles (<30 µm) and another fraction comprised of very large particles (⩾1000 µm).
The liberation of the olivine grains differed markedly between Pap and Ric sediments (figure 4(b)). In the Ric samples, ∼70 wt.% of the olivine grains showed a low liberation (<10% free surface), while only ∼10 wt.% were highly liberated (>90% free surface). In contrast, at Pap, the olivine grains showed markedly higher liberation, with ∼10–12 wt.% exhibiting <10% free surface and 30–50 wt% being highly liberated (>90% free surface). In Papakōlea, the olivine was mainly embedded in augite (74–83 wt.%). In Richardson Ocean Park, however, olivine was frequently bound to iron oxides such as goethite (28–39 wt.%) and hematite (6–13 wt.%; table 2).
Table 2. Minerals associated with olivine in Papakōlea A, B, and E and Richardson B, C and D (in wt %).
| Mineral associated with olivine | Pap-E | Pap-A | Pap-B | Ric-B | Ric-C | Ric-D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Augite | 74.15 | 74.18 | 82.9 | 48.6 | 48.2 | 44.3 |
| Goethite | 2.39 | 0.93 | 5.80 | 27.8 | 39.2 | 33.9 |
| Chromite | 10.10 | 5.83 | 4.62 | 8.06 | 0.72 | 0.51 |
| Hematite | 1.04 | 0.20 | 1.42 | 7.52 | 6.15 | 12.6 |
| Plagioclase | 1.03 | 3.52 | 1.16 | 1.83 | 2.13 | 1.35 |
| Calcite | 0.98 | 1.39 | 1.00 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 1.29 |
| Chlorite | 0.39 | 2.36 | 0.74 | 0.39 | 0.14 | 0.26 |
| Other | 0.03 | 4.89 | 0.17 | 1.46 | 0.80 | 0.34 |
| Free particles | 9.24 | 9.12 | 2.23 | 3.87 | 1.92 | 5.63 |
3.4. Weathering signatures in pore water depth profiles
Vertical profiles of pore water chemistry revealed distinct trends between the basaltic Pap site and the carbonate-dominated Ric site (figure 5), reflecting differing mineral dissolution dynamics. At Pap, increases in AT and dissolved silica (H4SiO4) with depth suggest active solute release consistent with silicate weathering processes, such as olivine dissolution. DO declined rapidly below the surface, while nickel (Ni) was elevated in surface layers. In contrast, the oxygen concentration at Richardson remained high at depth, suggesting substantial flushing of the pore water. The solute concentrations exhibited relatively little variation with depth, with lower concentrations of DSi and AT compared to Pap. The DSi and Ni at Pap only revealed a slight accumulation with depth. The pore water pH remained relatively constant with depth at both sites and attained slightly higher values at Ric.
Figure 5. Pore water concentrations at different in-situ locations at Pu’u Mahana Bay, Papakōlea (top) and Richardson Ocean Park (bottom). Points represent the mean concentrations at each depth and the error bars indicate standard deviations.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image 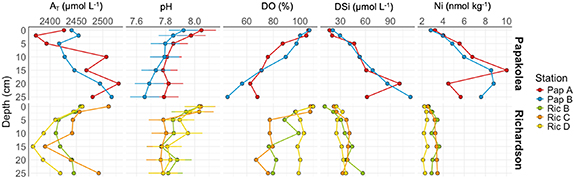
4.1. Contrasting olivine weathering mechanisms
Olivine-based mERW comprises a particular form of OAE that aims to achieve CDR by deposition of olivine sand onto the seafloor in coastal environments (Meysman and Montserrat 2017, Geerts et al 2025). In these applications, olivine sand will be mixed into the resident sediment, after which the olivine grains will chemically dissolve and release AT. The Hawaiian sediments investigated contained a substantial fraction of olivine (Papakōlea 68–92 wt. %; Richardson 12–31 wt. %; figure 4), and as such, these sites qualify as natural analogues for olivine-based mERW. While the olivine fraction in sediments subjected to mERW application might not be as high, the investigation of the geochemistry of the Pap and Ric sites can provide critical baseline insights into MRV strategies for OAE.
Marked differences between sites in the surface features of retrieved olivine grains suggest that different physical processes were influencing the weathering at Pap and Ric. Seabed ripples (figure S2) and visual observations during fieldwork indicate that bedload transport is an important process at Papakōlea (van Heurck et al 2025). In accordance with these observations, the olivine grains retrieved from the Pap sediment were smaller and considerably more rounded than olivine grains collected from the Pu’u Mahana cliffs (figure 2). As such, we suggest that physical abrasion during bedload transport is the main olivine weathering mechanism at Pap. In contrast, the more prominent edges of the olivine grains in the Ric sediments (figure 2) indicated that chemical dissolution and microbially mediated weathering was the dominant driver at this site, likely facilitated by elevated organic matter supply given the proximity of coral reef habitats. The high sediment permeability and strong advective ventilation at Ric resulted in deep pore water oxygenation (figure 5, Van Heurck et al 2025) also counteracting the accumulation of dissolved weathering products (AT, DSi) in the pore water, thus promoting mineral dissolution (Meysman and Montserrat 2017). Neither serpentinite nor sepiolite were detected, suggesting congruent olivine dissolution.
The contrasting weathering mechanisms at Pap and Ric were also reflected by differences in mineral association and physical disaggregation. The high degree of mineral liberation at Pap is in accordance with intense physical abrasion. In some cases, augite adheres to olivine grains providing some protection against chemical weathering. Yet in the so-called ‘coastal mill’, hydrodynamic sorting favors the liberation of dense olivine from lighter pyroxene fragments, which are more easily removed from the near-shore environments. This process accounts for the enrichment of olivine in the beach sands (Van Gosen et al 2014). In Ric, the degree of liberation was considerably lower and the olivine was frequently bound to iron oxides such as goethite and hematite (table 2). These oxides are formed through precipitation of the iron derived from the olivine itself as well as other sources, and they can form persistent coatings that inhibit dissolution (Rigopoulos et al 2018, Fuhr et al 2022, Geerts et al 2025). The lower hydrodynamic energy and pore water flushing at Richardson may increase the retention of iron in the bay, causing a higher rate of iron oxide precipitation on the olivine grains.
4.2. Alkalinity release from the sediment
As observed in flow-through incubations, the sediments at Pap and Ric seem to act as an important AT source to the overlying water, providing high potential release rates (20–140 mmol m−2 d−1; figure 2). These rank amongst the highest AT effluxes observed in coastal environments (typical 5–20 mmol m−2 d−1; van de Velde et al 2025 and references therein). This high release rate is however not apparent from the in situ pore water data, which do not show any marked AT accumulation with depth (figure 5). These two observations can be reconciled by the fact that the sediments investigated are coarse-grained and highly permeable, and thus are subject to strong physical ventilation, as signified by the deep oxygenation (figure 5). This strong advection impedes the accumulation of dissolution products within the pore water and hence masks any AT release from the sediment.
Net production of AT can stem from three sedimentary processes: weathering of silicate minerals (including olivine), carbonate dissolution and anoxic mineralization processes (denitrification and sulfate reduction followed by iron sulfide precipitation, Soetaert et al 2007, Middelburg et al 2020). A challenge for mERW is therefore to discern the AT generated by mineral addition from the naturally produced AT (Bach 2024, Geerts et al 2025). Given that the pore waters in these permeable sediments were oxygenated, the prevalence of anoxic mineralization is likely limited. Below, we assess whether the sedimentary fluxes of Ca, DSi and Ni can be used to estimate the AT contribution from carbonate dissolution (releasing Ca) versus olivine weathering (releasing DSi and Ni).
Carbonate minerals were present at all sites, and hence, a sedimentary Ca efflux can be interpreted as a sign of CaCO3 dissolution, which has a theoretical 2:1 AT:Ca ratio (figure 6). High Ca fluxes, consistent with CaCO3 dissolution, were observed at Ric C where the sediments consisted of ∼70% carbonates (figures 2 and 6). However, quantifying small changes in Ca concentrations against the high natural background is analytically challenging, and so the Ca fluxes presented in this study should only be seen as indicative. Still, we conclude that CaCO3 dissolution substantially contributed to the AT production at least at Ric C, but plausibly also at other sites.
Figure 6. Accumulation of alkalinity (AT) in the flow-through incubations relative, dissolved silica (DSi), dissolved nickel (Ni) and dissolved calcium (Ca). The dots indicate the different replicates and the dashed lines show ratios of 1DIC:1AT, 1DSi:3.73AT (olivine dissolution), 0.0061Ni:3.73AT (stoichiometric ratio in olivine grains from Aheim), and 1Ca:2AT (calcium carbonate dissolution).
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image 
Dissolved silica can originate from biogenic silica dissolution or silicate weathering. At Pap B and all the Ric stations, the flux ratio of DSi to AT was lower than the theoretical olivine dissolution ratio (∼0.27 mol:mol, figure 6). This suggests that a considerable fraction of the AT originated from CaCO3 dissolution, or that DSi from olivine dissolution was retained in the sediment, either via adsorption onto solid phases or clay formation (Lupker et al 2012, Ramos et al 2024), or that it was consumed by diatoms within the microbial film at the sediment surface (figure S6, Chisholm et al 1978). Furthermore, the DSi fluxes did not reflect the amount of olivine in the sediment (figures 2 and 4(a)). Due to the high turnover of DSi in natural systems, we agree with previous studies (Fuhr et al 2023, 2024) that sedimentary DSi fluxes are not a suitable proxy for olivine dissolution.
Hawaiian olivine is unusually Ni-rich (0.25–0.6 wt%) compared to typical basaltic olivine (Lynn et al 2017). Given the extremely low background concentration of Ni in seawater (∼2 nmol kg−1 in the upper 100 m, Bruland 1980, Middag et al 2020), even modest olivine dissolution should yield a measurable Ni signal. At both Pap B and Ric C, the observed sedimentary Ni:AT efflux ratio was considerably lower than expected if these fluxes had been driven solely by olivine dissolution (figure 6). While there likely were additional AT sources at these sites, Ni from olivine may also have been retained in the sediment as it is particle reactive and can adsorb to manganese and iron oxides (Bruggmann et al 2024). Interestingly, the Ni release was higher at Ric C than at Pap B (figure 2). Nickel is an essential micronutrient for algae and bacteria (Ciscato et al 2018), so the Ni at Ric C may stem partly from organic matter degradation, reflected by the higher sedimentary chlorophyll a content at this site (van Heurck et al 2025). However, it is also possible that the olivine weathering rate was higher in the incubations from Ric C, where pore water chemistry likely was the main driver of dissolution (section 4.1). Since bedload transport seems to have been important for the olivine weathering at Pap B, the exclusion of this mechanism in the flow-through incubations may have diminished down the observed weathering rates. As such, due to interference from other processes, the sedimentary Ni release cannot be used to quantify olivine dissolution in natural systems (Fuhr et al 2023, 2024) but could potentially indicate the relative importance of the process.
4.3. Implications for MRV and environmental assessments
While olivine dissolution has been studied extensively in controlled laboratory conditions, quantifying the AT release from mERW with olivine in natural systems is considerably more challenging (Fuhr et al 2023, Bach 2024, Fuhr et al 2024, Fuhr et al 2025, Geerts et al 2025). Prior laboratory experiments studying the dissolution of purified olivine grains suspended in solution have suggested that accumulation of solutes such as DSi and Ni can be used to track olivine dissolution kinetics (Berelson et al 2019). In agreement with microcosm studies of mERW with sediments (Fuhr et al 2023, 2024), we found that the use of these tracers may be confounded by the spatial heterogeneity, low abundances of Ni, and complex geochemical cycling occurring in natural sediments. In future studies, the stable isotope compositions of Si and Ni in sediment-water fluxes, pore waters and the solid phase might be used as geochemical tracers and strengthen process attribution and verification (Geerts et al 2025). Additionally, other AT generating processes in the sediment must be constrained in parallel to accurately quantify the AT release from olivine weathering. To this end, measurements of the stable isotope composition of DIC in incubations without atmospheric exchange could be used to more accurately estimate the contribution of CaCO3 dissolution to the AT flux (Berelson et al 2019).
As demonstrated by the high solute fluxes despite low pore water accumulation (figures 2 and 5), it is critical to perform suitable rate measurements (AT release rates) in addition to pore water depth profiles when olivine-based mERW is applied in permeable sediments. However, flow-through incubations also face challenges in mimicking the natural sediment structure and may disrupt natural transport limitations, thus altering redox conditions and microbial activity. A detailed understanding of the targeted environment is therefore required to achieve incubation conditions that are representative of the natural state. Furthermore, the effects of wave action on olivine weathering must be measured in alternative setups aimed at simulating bedload transport (Gunter et al 2023, England and Bach 2025). Clear signs of physical weathering were seen on olivine grains exposed to bedload transport at Papakōlea (figure 3), yet olivine dissolution was not obvious from the flow-through incubations (figure 2). Consequently, the detailed analysis of mineral grains—as performed here—thus provides valuable information about dissolution processes and potential reactivity and should be incorporated in MRV programs. Surface analysis of olivine grains using electron microscopy later can reveal dissolution features such as pit density and rounding offering clear visual evidence of weathering. Here, this approach was applied to compare the fresh cliff face olivine particles to the found at the submerged sites. In mERW applications this can be applied to compare the initial ‘fresh’ source material to particles that are recovered years after from the mERW site. A robust approach for assessing the environmental fate of Ni will be needed before olivine can be used in mERW applications. Elevated Ni concentrations in the pore water at Pap B (figure 5), especially in the deeper layers, suggest it might stem from olivine dissolution. However, despite increasing AT concentrations in the flow-through experiments, the Ni fluxes at Pap B and Ric C were low (figures 2 and 6). Since Ni can be retained in olivine, re-adsorbed to mineral surfaces, or incorporated into secondary minerals (Palandri and Reed 2004, Majumdar et al 2014, Bruggmann et al 2024), much of it may remain immobilized locally. This limited mobility suggests low ecological impact on ecosystems from olivine-based mERW, even in warm, organic-rich nearshore environments (Flipkens et al 2021, Gunter et al 2023, Jankowska et al 2024). However, future studies should quantify Ni in different solid phases to assess its mobility, which likely will depend on site-specific conditions.
Our study of Papakōlea and Richardson, Hawai’I, highlights key challenges and opportunities in understanding olivine weathering within a natural context and its implications for OAE and mERW projects. The natural olivine-rich beaches of Hawai’i act as a natural analogue and provide a rare opportunity to study long-term silicate weathering under real-world conditions. This way, they can offer crucial insights into the safety and efficiency of OAE strategies that would take decades to replicate in controlled experiments. Our results highlight that olivine weathering takes place with a natural environment, which shows considerable hydrodynamic and biogeochemical complexity. This makes the quantitative assessment of weathering rates challenging, and as a result, it is difficult to differentiate the alkalinity signal from mERW from that of the resident natural processes that also release alkalinity. Future work should refine weathering tracers, assess biogeochemical feedback, and explore regional differences in dissolution dynamics to better inform OAE implementation. Understanding natural analogs like Papakōlea Beach will be essential in evaluating the long-term feasibility and ecological risks of enhanced silicate weathering as a climate mitigation strategy.
Field research for this project was conducted under Hawaii Department of Land and Natural Resources special activities permit SAP 2023-15. No destructive analyses were conducted and all sand was returned to the sampling sites after analysis. We thank representatives of the Hawaii Department of Land and Natural Resources as well as numerous local Hawai’ian community members for supporting this work. Funding for this project was provided by Vesta, PBC, through a charitable donation from the Green Dividend Program of Alstria REIT-AG (Hamburg, Germany). Additional support was provided by a Strategic Basic Research (SBO) project from FWO (project no. S000619N) and the VLAIO De Blauwe Cluster project ‘Blue Alkalinity’ (HBC.2023.0496). AH was supported by a junior postdoctoral fellowship from FWO (project 1241724N). The SEM instrumentation in Belgium used in this study received funding from Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO) for medium-scale research infrastructure under grant agreement number I013118N. Field work for Nicolaysen and Barnett as well as XRD single grain analyses and SEM surficial imaging at Whitman College were supported by a Faculty-Student Summer Research award to Nicolaysen and Barnett. We thank the Geobiology Research Group, from the University of Antwerp, especially Cedric Goossens and Saïd De Wolf for support and QMineral (Leuven, Belgium) for providing XRD-based mineralogical composition data.
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article (and any supplementary files).
Funding for this study was provided by Vesta, PBC, which is conducting research and development of mERW approaches for eventual commercial deployment. SJR is a full-time employee of Vesta, PBC. DBC was a full-time employee of Vesta, PBC, from 1 January 2022, to 14 May 2024, before moving to the non-profit Hourglass Climate full-time on 15 May 2024. All experimental designs, data, analysis, and conclusions have been reviewed by all authors to ensure accuracy and impartiality.