In a recent post, The Quirks of Index Maintenance in Open Source Databases, I compared the IO load generated by open source databases while inserting rows in a table with many secondary indexes. Because of its change buffer, InnoDB was the most efficient solution. However, that’s not the end of the story.
Evolution of the InnoDB doublewrite buffer
Up until a few years ago, the InnoDB doublewrite buffer was a bottleneck under high write load. Essentially, the doublewrite buffer is a file used to prevent torn pages. InnoDB uses 16KB pages, which can easily be partially written (torn) in case of a crash (Example: The storage device uses 4KB blocks. This requires 4 IO to write a page. If a crash occurs after 2 IO, then a co…
In a recent post, The Quirks of Index Maintenance in Open Source Databases, I compared the IO load generated by open source databases while inserting rows in a table with many secondary indexes. Because of its change buffer, InnoDB was the most efficient solution. However, that’s not the end of the story.
Evolution of the InnoDB doublewrite buffer
Up until a few years ago, the InnoDB doublewrite buffer was a bottleneck under high write load. Essentially, the doublewrite buffer is a file used to prevent torn pages. InnoDB uses 16KB pages, which can easily be partially written (torn) in case of a crash (Example: The storage device uses 4KB blocks. This requires 4 IO to write a page. If a crash occurs after 2 IO, then a complete page was not written, and is now torn). When a dirty page in the InnoDB buffer needs to be flushed to storage, the following steps are executed:
- First, a slot (or many) from the doublewrite buffer is acquired
- The dirty page is first written to the doublewrite buffer file
- The doublewrite buffer file is fsync’d
- The page is then written to its tablespace file
- The tablespace file is fsync’d
- Finally, the doublewrite buffer slot is released
Above, I discussed flushing a single page, but most of the time, more than one page is flushed together. The main issue is that there are only about 120 slots, and between steps one and six, one or many slots are locked. That essentially limits the number of write operations in-flight. On storage devices with a significant latency, like network-attached cloud storage, this represents a major bottleneck for writes.
To fix this, Percona introduced in Percona Server for MySQL 5.7.11 the parallel doublewrite buffer, where every buffer pool instance got a full doublewrite buffer with 120 slots. This greatly improved the flushing capacity, allowing a vastly superior number of in-flight write operations. Realizing the benefits of the Percona parallel doublewrite buffer, Oracle implemented a similar feature in MySQL 8.0.20. Their implementation has the added advantage of allowing you to set the size of the doublewrite buffers. It is, however, with this added degree of liberty that a poor choice of a default value was made. Instead of going with a choice similar to the Percona implementation of 120, they chose to default to the number of write IO threads. The default number of write IO threads is four, a tiny value for the doublewrite buffer.
The Oracle implementation was shown by Dimitry (here) to have very positive impacts. The performance results are much better than the old single doublewrite buffer. But, as shown here by Vadim, there is still a bottleneck around the doublewrite buffer. The fix is easy: just set innodb_doublewrite_pages to 128 (jfgagne and MySQL 8.0 doc).
Impacts on the IO results
So, what would be the impacts on my earlier results? Well, the impacts are hard to miss…
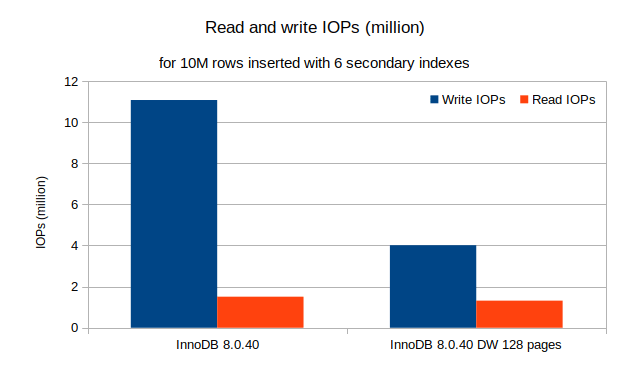
Impacts of doublewrite page size default value
The number of write IOPs is down by almost two-thirds (64%), and the number of read IOPs is reduced by 13%. This large difference is likely caused by the low concurrency I used to generate the IOPS, a single insert thread. Nevertheless, replication is often also fairly low on concurrency.
This leaves me puzzled. I know the default value issue is fixed in 8.4.x, but I still have many customers who have just completed their migration to 8.0.x. Why would a one-liner patch to 8.0 not be included in the 8.0.43 release last July? Vadim’s post More on Checkpoints in InnoDB MySQL 8, describing the issue dates from 2020; nothing is new here. Given the lack of will to address the issue upstream, despite acknowledging it in the documentation, I filed a request in our own Jira (PS-10236) to at least fix Percona Server for MySQL 8.0.x.