getting lit
We didn’t start the fire. (Neanderthals did, at least 400,000 years ago.)
This artist’s impression shows what the fire at Barnham might have looked like. Credit: Craig Williams, The Trustees of the British Museum
Heat-reddened clay, fire-cracked stone, and fragments of pyrite mark where Neanderthals gathered around a campfire 400,000 years ago in what’s now Suffolk, England.
Based on chemical analysis of the sediment at the site, along with the telltale presence of pyrite, a mineral not naturally found nearby but very handy for striking sparks with flint, British Museum archaeologist Rob Davis and his colleagues say the Neanderthals probably started the fire themselves. That makes the abandoned English clay pit at Barnham the oldest evidence in the world that people …
getting lit
We didn’t start the fire. (Neanderthals did, at least 400,000 years ago.)
This artist’s impression shows what the fire at Barnham might have looked like. Credit: Craig Williams, The Trustees of the British Museum
Heat-reddened clay, fire-cracked stone, and fragments of pyrite mark where Neanderthals gathered around a campfire 400,000 years ago in what’s now Suffolk, England.
Based on chemical analysis of the sediment at the site, along with the telltale presence of pyrite, a mineral not naturally found nearby but very handy for striking sparks with flint, British Museum archaeologist Rob Davis and his colleagues say the Neanderthals probably started the fire themselves. That makes the abandoned English clay pit at Barnham the oldest evidence in the world that people (Neanderthal people, in this case) had learned to not only use fire, but also create it and control it.
A cozy Neanderthal campfire
Today, the Barnham site is part of an abandoned clay pit where workers first discovered stone tools in the early 1900s. But 400,000 years ago, it would have been a picturesque little spot at the edge of a stream-fed pond, surrounded by a mix of forest and grassland. There are no hominin fossils here, but archaeologists unearthed a Neanderthal skull about 100 kilometers to the south, so the hominins at Barnham were probably also Neanderthals. The place would have have offered a group of Neanderthals a relatively quiet, sheltered place to set up camp, according to Davis and his colleagues.
The cozy domesticity of that camp apparently centered on a hearth about the size of a small campfire. What’s left of that hearth today is a patch of clayey silt baked to a rusty red color by a series of fires; it stands out sharply against the yellowish clay that makes up the rest of the site. When ancient hearth fires heated that iron-rich yellow clay, it formed tiny grains of hematite that turned the baked clay a telltale red. Near the edge of the hearth, the archaeologists unearthed a handful of flint handaxes shattered by heat, alongside a scattering of other heat-cracked flint flakes.
And glinting against the dull clay lay two small pieces of a shiny sulfide mineral, aptly named pyrite—a key piece of Stone Age firestarting kits. Long before people struck flint and steel together to make fire, they struck flint and pyrite. Altogether, the evidence at Barnham suggests that Neanderthals were building and lighting their own fires 400,000 years ago.
Fire: the way of the future
Lighting a fire sounds like a simple thing, but once upon a time, it took cutting-edge technology. Working out how to start a fire on purpose—and then how to control its size and temperature—was the breakthrough that made nearly everything else possible: hafted stone weapons, cooked food, metalworking, and ultimately microprocessors and heavy-lift rockets.
“Something else that fire provides is additional time. The campfire becomes a social hub,” said Davis during a recent press conference. “Having fire… provides this kind of intense socialization time after dusk.” It may have been around fires like the one at Barnham, huddled together against the dark Pleistocene evening, that hominins began developing language, storytelling, and mythologies. And those things, Davis suggested, could have “played a critical part in maintaining social relationships over bigger distances or within more complex social groups.” Fire, in other words, helped make us more fully human and may have helped us connect in the same way that bonding over TV shows does today.
Archaeologists have worked for decades to try to pinpoint exactly when that breakthrough happened (although most now agree that it probably happened multiple times in different places). But evidence of fire is hard to find because it’s ephemeral by its very nature. The small patch of baked clay at Barnham hasn’t seen a fire in half a million years, but its light is still pushing back the shadows.
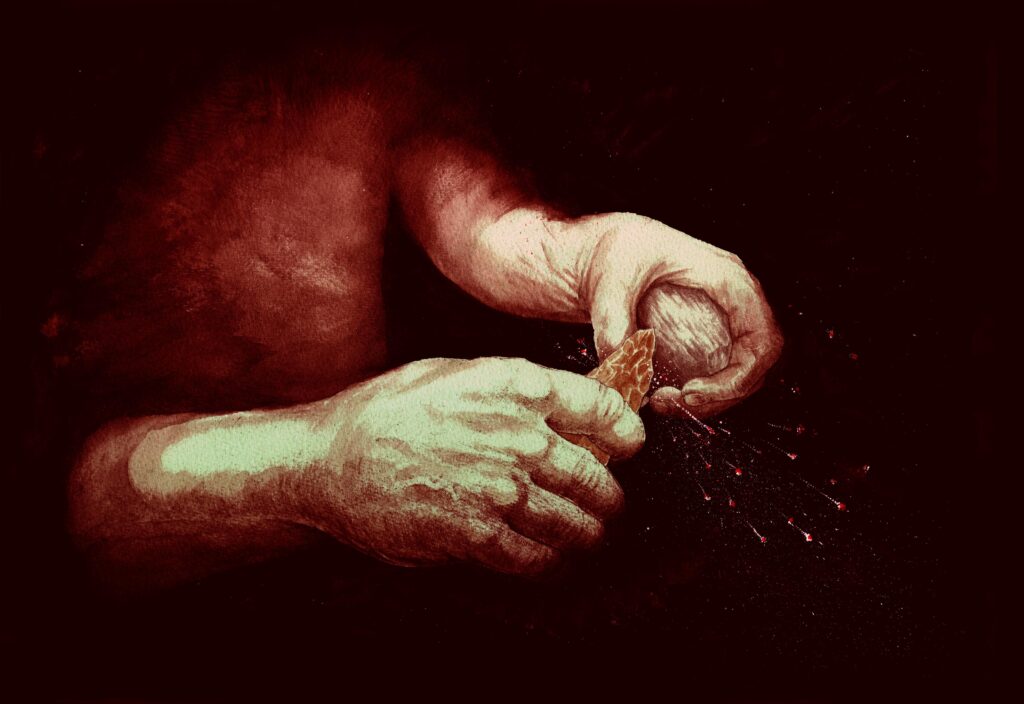
This was the first step toward the Internet. We could have turned back. Credit: Craig Williams, The Trustees of the British Museum
A million-year history of fire
Archaeologists suspect that the first hominins to use fire took advantage of nearby wildfires: Picture a Homo erectus lighting a branch on a nearby wildfire (which must have taken serious guts), then carefully carrying that torch back to camp to cook or make it easier to ward off predators for a night. Evidence of that sort of thing—using fire, but not necessarily being able to summon it on command—dates back more than a million years at sites like Koobi Fora in Kenya and Swartkrans in South Africa.
Learning to start a fire whenever you want one is harder, but it’s essential if you want to cook your food regularly without having to wait for the next lightning strike to spark a brushfire. It can also help maintain the careful control of temperature needed to make birch tar adhesives, “The advantage of fire-making lies in its predictability,” as Davis and his colleagues wrote in their paper. Knowing how to strike a light changed fire from an occasional luxury item to a staple of hominin life.
There are hints that Neanderthals in Europe were using fire by around 400,000 years ago, based on traces of long-cold hearths at sites in France, Portugal, Spain, the UK, and Ukraine. (The UK site, Beeches Pit, is just 10 kilometers southwest of Barnham.) But none of those sites offer evidence that Neanderthals were making fire rather than just taking advantage of its natural appearance. That kind of evidence doesn’t show up in the archaeological record until 50,000 years ago, when groups of Neanderthals in France used pyrite and bifaces (multi-purpose flint tools with two worked faces, sharp edges, and a surprisingly ergonomic shape) to light their own hearth-fires; marks left on the bifaces tell the tale.
Barnham pushes that date back dramatically, but there’s probably even older evidence out there. Davis and his colleagues say the Barnham Neanderthals probably didn’t invent firestarting; they likely brought the knowledge with them from mainland Europe.
“It’s certainly possible that Homo sapiens in Africa had the ability to make fire, but it can’t be proven yet from the evidence. We only have the evidence at this date from Barnham,” said Natural History Museum London anthropologist Chris Stringer, a coauthor of the study, in the press conference.
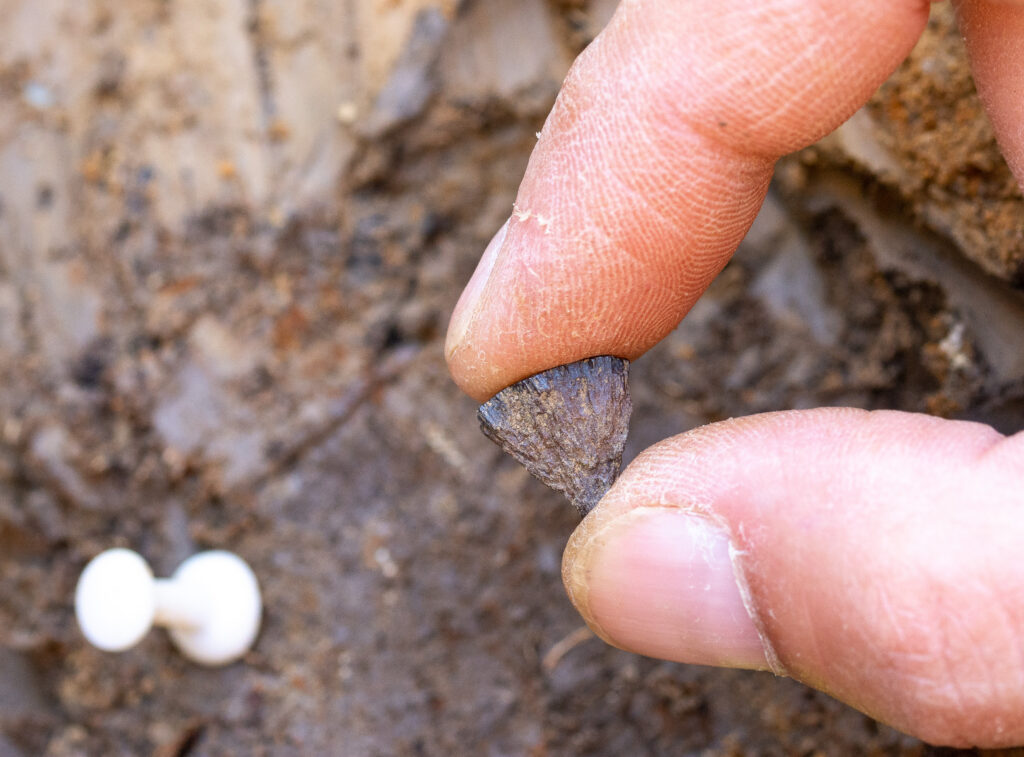

The two pyrite fragments at the side may have broken off a larger nodule when it was struck against a piece of flint. Credit: Jordan Mansfield, Pathways to Ancient Britain Project.
Digging into the details
Several types of evidence at the site point to Neanderthals starting their own fire, not borrowing from a local wildfire. Ancient wildfires leave traces in sediment that can last hundreds of thousands of years or more—microscopic bits of charcoal and ash. But the area that’s now Suffolk wasn’t in the middle of wildfire season when the Barnham hearth was in use. Chemical evidence, like the presence of heavy hydrocarbon molecules in the sediment around the hearth, suggests this fire was homemade (wildfires usually scatter lighter ones across several square kilometers of landscape).
But the key piece of evidence at Barnham—the kind of clue that arson investigators probably dream about—is the pyrite. Pyrite isn’t a naturally common mineral in the area around Barnham; Neanderthals would have had to venture at least 12 kilometers southeast to find any. And although few hominins can resist the allure of picking up a shiny rock, it’s likely that these bits of pyrite had a more practical purpose.
To figure out what sort of fire might have produced the reddened clay, Davis and his colleagues did some experiments (which involved setting a bunch of fires atop clay taken from near the site). The archaeologists compared the baked clay from Barnham to the clay from beneath their experimental fires. The grain size and chemical makeup of the clay from the ancient Neanderthal hearth looked almost exactly like “12 or more heating events, each lasting 4 hours at temperatures of 400º Celsius or 600º Celsius,” as Davis and his colleagues wrote.
In other words, the hearth at Barnham hints at the rhythms of daily life for one group of Neanderthals 400,000 years ago. For starters, it seems that they kindled their campfire in the same spot over and over and left it burning for hours at a time. Flakes of flint nearby conjure up images of Neanderthals sitting around the fire, knapping stone tools as they told each other stories long into the night.
Nature, 2025 DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09855-6 [About DOIs](https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09855-6;%20(<a%20href=)).
Kiona is a freelance science journalist and resident archaeology nerd at Ars Technica.